Stelsel vergelijkingen oplossen met een grafische rekenmachine#
Een stelsel vergelijkingen in de vorm \(Ax=b\) kan worden opgelost met een grafische rekenmachine.
Example
Laten we een voorbeeld bekijken
Definieer de aangevulde matrix \(\left[A|b\right]\) door aaneenschakeling van \(A\) en \(b\) met \(b\) aan de rechterkant.
Example
De aangevulde matrix van ons voorbeeld is:
\[\begin{split}\left[\begin{array}{cccccccc}0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & - \frac{4}{1875} & - \frac{1}{625} & -4 & 1 & -\frac{8}{375}\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \frac{1}{625} & \frac{1}{1250} & 1 & 0 & \frac{8}{375}\\- \frac{4}{1875} & - \frac{1}{625} & -4 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\\frac{1}{625} & \frac{1}{1250} & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\4 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\end{array}\right] \end{split}\]Dit kan worden gedefinieerd in een grafische rekenmachine (TI-84 als voorbeeld):
Fig. 111 Open het matrix menu:
2nd-matrix#
Fig. 112 Ga naar
EDIT#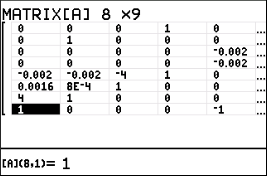
Fig. 113 Bewerk de eerste matrix#
Reduceer/veeg de matrix per rij, de oplossing voor \(x\) is de meest rechtse kolom van de matrix.
Example
De gereduceerde matrix ziet er als volgt uit:
\[\begin{split} \left[\begin{array}{cccccccc}1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 4.375\\0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & -0.006667\\0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 4.375\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 17.5\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0.0003333\\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0.01733\end{array}\right]\end{split}\]Dus:
\[\begin{split} \left[ \begin{array}{cccccccc} C_1\\C_2\\C_3\\C_4\\C_5\\C_6\\C_7\\C_8 \end{array} \right] = \left[\begin{matrix}4.375\\0\\-0.006667\\0\\4.375\\17.5\\0.0003333\\0.01733\end{matrix}\right] \end{split}\]Dit kan worden gevonden op een grafische rekenmachine:
Fig. 114 Gebruik het
rref(commando inmatrix-MATH#
Fig. 115 Evalueer
rref(A)#
Figuren gemaakt met https://ti84calc.com/ti84calc
